What are Compression Tube Socks?
Compression tubes are elastic garments that you can use to compress swollen limbs, cover wounds, and hold dressings in place. They help reduce swelling that causes pain. Tube legs provide lasting support that will not restrict joint movement.
What is the Ideal Pressure Level?
The level of compression required for treating various conditions differ. Compression is measured in mmHG, or milimeters of Mercury, the same measuring convention used when taking blood pressure. Compression ranges from 8-15 mmHG to 20-30 mmHg to Extra Firm 30-40 mmHg depending on the level of compression needed. The compression created by ComproGear compression tube socks adds pressure to the legs to force blood back into the upper body using 20-30 mmHg compression level. We feel this is the best option for most people.
Low, Medium, and High Support Leg Tube Compression
Compression tubes can have mild, moderate, firm or extra firm pressure levels. For example, for treatment of venous ulcerations in your lower extremities, you may need a pressure level of about 40 mmHg. The following conditions would require higher compression:
- Venous ulceration
- Swollen with edema
- Venous deficiency
- Vericose veins
- Post Thrombotic Syndrome (PTS)
- Edema and lymphedema
What Conditions Do They Help Treat or Manage?
Wound Care
A compression tube plays an important role in wound management. It helps protect your skin from contact sensitivity while keeping creams and dressings in place. Regardless the fact that many dressings have adhesive backing, tubular bandages offer reliable reinforcement. Tubes that are correctly applied can provide a comfortable and safe alternative to dressings or adhesives. But use caution when applying tubes. Poor technique during application can increase localized pressure, causing pain. According to research, these elastic garments should conform properly to the contours of your limbs in order to allow for free movement of your joints. Risk factors may include:
- Poor circulation
- Decreased immobility or mobility
- Suppressed or compressed immune system
- Obesity
Venous Ulcers
With venous leg ulcers, there is usually a valve dysfunction of the veins. This may be due to increased pressure, failure of the calf pumps, and congenital varicose veins. In venous ulcers stasis of the blood occurs. Fuid leaks from the veins under the skin causing an ulceration on the surface of the skin. If this condition is not treated, it can cause sensory neuropathy or trauma. You may also develop small muscle wasting which can significantly cause tearing in your toes. Venous ulcerations and preceding skin changes are best managed by careful evaluation of the venous system of the lower limb accompanied by compression bandaging and stockings. Topical applications are broadly used in the management of leg ulceration but a surgical procedure is suitable where the ulceration is based on superficial venous incompetence alone. In some studies, surgical interventions would apply to as many as half the people presenting with venous ulcerations on the lower extremities. However, most studies have shown that the condition can be best managed by compression treatment. Symptoms of this condition may include:
- Swollen ankles
- Swelling or aching legs
- Darkening and discoloration of the skin
- Itchy, flaky, red, scaly skin
- Foul-smelling discharge
Economy Class Syndrome
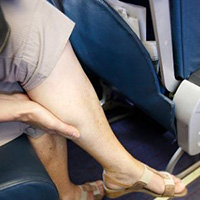

This may occur when people do not move enough while sitting in a confined space for a long duration, such as in a plane, when the legs remain bent for a long time. The cramped conditions cause the blood circulation in the veins in the back of your limbs to be poor, and can lead to the formation of blood clots. Experts believe that as long as you maintain a fixed sitting position with your knees bent and remain immobile for more than four hours, you odds of getting the condition are high. Compression tubing provides homogeneous pressure as well as contact support. This will help facilitate deep vein circulation during long hours of sitting. The symptoms of this condition may vary from one person to another, but the most common symptoms are:
- Dizziness
- Sharp chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Panic attacks
Venous Insufficiency
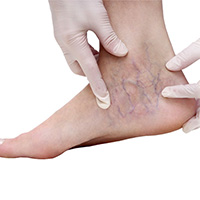
This is a condition in which lower extremity venous hypertension occurs due to abnormalities of the venous valves or walls. This usually happens at the onset of prior deep vein thrombosis, but it can arise from an unknown cause or factor. Varicose veins are the most common manifestation of venous insufficiency and are believed to affect approximately thirty percent of the adult population. Other symptoms include skin changes, ulceration, and edema. The typical presentation of the condition is eczema or scarring of the skin and fat on the legs. Tubular elastic compression devices provide graduated compression to manage the condition and the uniform continuous support boosts circulation in the limbs. Various symptoms of this condition are:
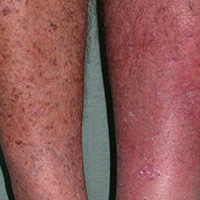
- Leg ulcers
- Varicose veins
- Skin changes
- Cramps
- Swelling
- Pain
Edema
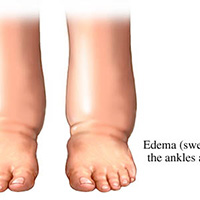
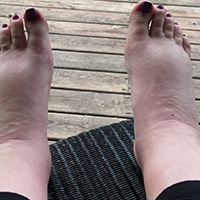
This refers to excessive accumulation of fluid in tissue spaces. Swelling of the feet, ankles, and legs causes them to feel heavy and bloated. Throughout the body, fluids usually pass back and forth between blood and tissue. When there is extra pressure in the veins of your legs, fluid is forced out of the blood and into the tissues. The most prevalent cause of excess pressure in the leg veins is gravity due to long periods of standing or because of changes in the body that are age related. Leg swelling also occurs during pregnancy, generally because the pressure of the enlarged uterus slows the return of blood from the leg veins to the heart. If you are pregnant, persistent, excessive swelling of your feet can indicate edema. You can manage this with compression tubes or discuss advanced care with your doctor. Although edema is seldom an emergency, it can sometimes signal an undetected medical problem, such as infection, blood clots or heart failure. There are various symptoms associated with this condition, including:
- Increased abdominal size
- Shiny or stretched skin
- Puffiness or swelling of the tissue underneath the affected part
There are two main types of edema, which include:
- Peripheral Edema
This is a condition that mainly affects your ankles, feet, and legs. It can indicate problems with kidneys, lymph nodes, or your circulatory system.
- Pedal Edema
You experience this condition when fluid shifts to your lower extremities. The main causes are lymphedema, a high-sodium diet, peripheral vascular disease, and lower extremity trauma.
Other Popular Articles on ComproGear
Rose Toy Best Toy Rose Adult Toy
Plus Size Compression Socks Extra Large Compression Socks & Bariatric Compression Socks
Sports Injuries


Physical injuries can be defined as any stress on the body that prevents a specific body part from functioning properly. A sports injury can be further defined as any kind of injury or damage that occurs as a result of exercise or sports. The following parts are affected in a sports injury:
- Muscles – Mainly composed of fat, glycogen, mineral salts, protein, and water
- Bones – Bones sit in cavities surrounded by circular layers of hard matrix
- Joints – Joints are made up of tendons, ligaments, bursa, and cartilage. They hold bones together and give them rigid skeleton mobility
- Cartilage – A specialized fibrous connective tissue which provides a smooth surface for the movement of joints. Catrilage absorbs impact and friction when bones bump and rub against each other
The symptoms of sports injury may include:

- Severe or sudden pain
- Extreme leg weakness
- Inability to move a joint
- Swelling
There are a number of considerations to take into account when searching for the best tubular devices, including:
How to Choose an Appropriate Size
There are different sizes of compression tubes. They can be used in more than one layer to increase both resting and ambulatory pressures. While these devices provide less pressure compared to compression stockings, we find them to be useful for people who cannot tolerate higher compression due to:
- Arterial insufficiency
- Tenderness
- Pain
- Or difficulty in application
Our ComproGear Compression Socks come in sizes up to 3X wide calf compression socks.
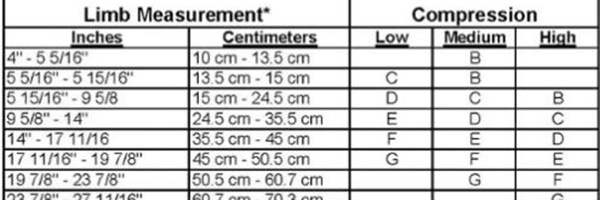
Using the Measuring Tape

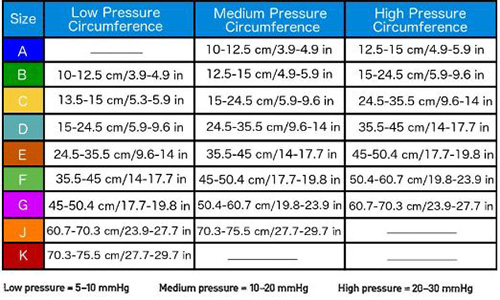
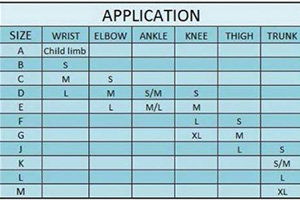
To choose the ideal size of compression tube, place the measuring tape around the widest part of the leg. Next, match the amount of pressure (high, medium, or low) with the size of the stocking required. Most manufacturers provide the following sizes (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, and K), which correspond to the tissue support circumference.
Size Ranges

Size Ranges include:
A – 3.9 to 4.9 and 4.9 to 5.9 inches,
B – 5.3 to 5.9, 4.9 to 5.9, and 5.9 to 9.6 inches
C – 5.3 to 5.9, 5.9 to 9.6, and 9.6 to 14 inches
D – 5.9 to 9.6, 9.6 to 14, and 14 to 17.7
E – 9.6 to 14, 14 to 17.7, 17.7 to 19.8
F – 14 to 17.7, 17.7 to 19.8, 19.8 to 23.9
G – 17.7 to 19.8, 19.8 to 23.9, 23.9 to 27.7
J – 23.9 to 27.7, 27.7 to 29.7
K – 27.7 to 29.7 inches
What are the Different Sizes Suitable For?
Here are the various uses of each different size of compression tubing:
- Sizes K, L, and J are ideal oversize thigh use
- Size G is ideal for large thigh
- Size F is ideal for medium thigh and large knee
- Size E is ideal for small thigh, medium knee, and large ankle
- Size D is ideal for small knee, medium ankle, elbow, and large wrist
- Size C is ideal for small ankle, elbow, and medium wrist
- Size B is ideal for small elbow and wrist
- Size A is ideal for child’s limb
Specific Features to Look For
Knowing the ideal size of the elastic tubular bandage to look for is not always sufficient. You should also consider performance features that will make the devices more useful to you.
Things to Look For:
Performance Features of Compression Tubes
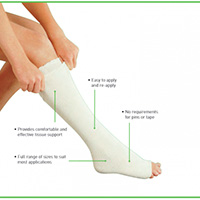
- Constant high-quality support with only one application
- Easy to use bandages without the need of a pin
- Must have hospital-grade quality that is guaranteed to offer relief
- Should be sufficiently long for effective application
Quality of Material for Compression Tubes
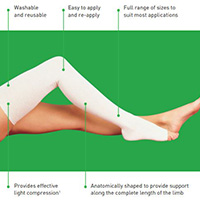
- Should be made of hypoallergenic material
- Should be soft, but very strong
- Non-abrasive
- Close fitting and easy to apply
Ease of Maintenance the Compress

- Should be machine washable
- Easy to wash colors
How to Apply Tubular Support Devices

Select the appropriate length of tubular bandage from the hollow of the knee to your toes. Add three inches for extremities. Apply the tubular device by rolling it up the leg to the knee. Place the compression tube along the side of the instep, parallel to the base of the toes. Insert a foam rubber pad to increase compression if needed. Continue to apply the padding up the leg in spiral turns with fifty percent overlap. The ankle circumference should be greater or equal to eighteen centimeters. Make sure to add enough lining to increase coverage if necessary.
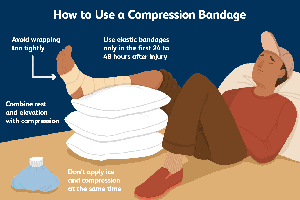
Apply the compress over the insertion point of the Achilles tendon, covering the first half of the heel. Bring the compression tube from the middle to the side ankle, covering the second half of the heel to reach the sole. Continue spiraling the bandage up the leg with fifty percent overlap and fifty percent stretch. If a second bandage is applied, start at the ankle and spiral in the opposite direction. Stop at a two-finger thicknesses below the knee. Secure the end of the compress with quality adhesive tape.
In Summary
Tubular support bandages are suitable for treating and preventing sports injuries, venous insufficiency, venous ulcers, edema, wounds, and economy class syndrome.
