Living with a health condition caused by an imbalance of enzymes in the bodily system can be hard. Fortunately, there are treatments available, including supplements, which can help reduce discomfort and other symptoms.
As there are more than one classifications of enzymes, this article focuses on digestive enzymes, which are meant to assist in speeding the reaction of breaking down food into absorbable nutrients.
Continue reading to learn more about enzymes, how they benefit us and the best digestive enzyme supplements.
What are Enzymes?

Enzymes are essentially biological catalysts, which mean they help increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. They have two fundamental properties: 1) increasing the rate of chemical reactions without being affected by them; and 2) increasing the rate of chemical reactions without altering the chemical equilibrium between the reactants and the products.
Why are Enzymes Important?

Enzymes are strongly important as that they enable chemical reactions at a rate necessary for life— in animals and human beings, this means supporting in the digestion of food and other critical functions.
In other words, we would not be able to function effectively without them because “the chemical reactions required to maintain the body simply would not occur fast enough.” Therefore, they play a highly centric role in every biochemical process.
There are, however, disorders that occur due to a deficiency or total absence of one or more enzymes, such as diabetes or Tay-Sachs disease, or excessive activity of one or more enzymes, such as cancer.
How do Enzymes Work?
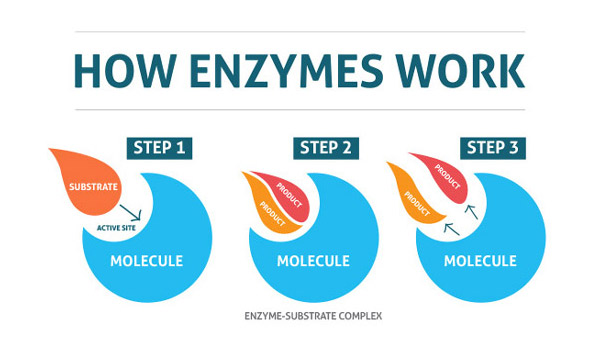
Based on the book The Cell: A Molecular Approach, 2nd edition by Cooper GM., the catalysis of enzymes is explained in which a “molecule acted upon by an enzyme (referred to as a substrate [S]) is converted to a product (P) as the result of the reaction. … In the presence of the appropriate enzyme, the conversion of S to P is accelerated, but the equilibrium between S and P is unaltered.”
Further explanation, quoted from the same source, is as follows:
“The catalytic activity of enzymes involves the binding of their substrates to form an enzyme-substrate complex (ES). The substrate binds to a specific region of the enzyme, called the active site. While bound to the active site, the substrate is converted into the product of the reaction, which is then released from the enzyme.”
What Types of Enzymes are There?
Most enzymes are proteins, however there are some that are not, such as ribozymes which are catalytic ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules and are involved in RNA processing.
According to the International Union of Biochemists (IUB), there are six classifications for enzymes, with each classification based on the type of reaction in which they are used to catalyze.
1. Oxidoreductases

As its name implies, these enzymes catalyzes an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction— in detailed terms, it “catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor.”
Due to its biodegradability, specificity and efficiency, it is highly useful in industrial applications and for synthesis, such as food and beverage improvement as well as medical and chemical synthesis.
2. Transferases
These enzymes help catalyze the transfer of one chemical group from one molecule compound to another; one example is the transaminase enzyme, which transfers an amino group from one molecule to another. These enzymes are not widely used in industrial processes.
3. Hydrolases
These enzymes help catalyze the hydrolysis of a chemical bond; one example is how the proteases enzyme hydrolyzes proteins to smaller peptides and then to amino acids, which turns them into proteins. The natural function for hydrolases is to carry out important degradative reactions in the body, which basically means that they help break down nutrients.
In this case, they help especially for digestion.
4. Lyases

These enzymes help in catalyzing addition and elimination reactions; one example is breaking the chemical bond between a carbon atom and an oxygen atom.
5. Isomerases

These enzymes catalyze reactions involving the structure of a molecules which share the same atomic composition but different arrangements of chemical groups. They are needed in proper metabolism function and are applicable in organic synthesis and biotechnology.
6. Ligases
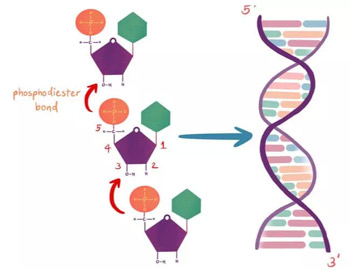
These enzymes catalyze the binding of two molecules by creating a new chemical bond; an example is a DNA lygase that link two fragments of DNA by forming a phosphodiester bond.
What are the Benefits of Digestive Enzymes?
Referring to the six classifications of enzymes as mentioned above, all digestive enzymes belong to the hydrolase class. They specifically help out in breaking down food into their ‘building block’ components, and mix with these components as they pass along the gut, so that the nutrients can be easily absorbed through the gut wall and into the bloodstream.
In the human body, the main digestive enzyme-producing structures are the salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, liver and small intestine. Each structure helps digest a different substance– for instance, the digestive enzyme produced in the salivary glands is the amylase, which digests starch into maltose, whereas the stomach produces gastric juice containing protease (pepsin) and hydrochloric acid, which digests proteins into partly digested proteins.
When normal functioning of these structures is disrupted, the body may be unable to properly break down food in the way mentioned above. Therefore, digestive enzyme supplements can be consumed to help prevent malabsorption; for example, it is not uncommon for physicians to prescribe Rx digestive enzymes to individuals with conditions like pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, and cystic fibrosis. Another common health condition is those who suffer from lactose intolerance— this is due to lacking the enzyme lactase.
Popular Articles on ComproGear
Rose Toy comprogear.com/rose-toy/
Compression Socks for Men comprogear.com/compression-socks-men/
Plus Size Compression Socks comprogear.com/plus-size-compression-socks/
Best Compression Socks for Edema comprogear.com/best-compression-socks-for-edema/
How Long to Wear Compression Socks for Edema comprogear.com/how-long-to-wear-compression-socks-for-edema/
Medical Compression Socks comprogear.com/medical-compression-socks/
What are the Best Digestive Enzymes?
Before purchasing and consuming any supplement, it is recommended to first consult with your doctor or physician, especially if you are pregnant or have any allergies.
Based on the reviews by health and wellness site Very Well Health, below are the highlighted best digestive enzymes currently on the market which can help ease stomach problems and treat indigestion. These products have been independently researched and tested by the editors at Very Well Health and the site may receive commissions on purchases made from their chosen links.
1. Best Overall – Pure Encapsulations Digestive Enzymes Ultra at swansonvitamins.com

This product is sold at a retail price of $54 for a one-time only delivery; subscriptions allow for additional benefits, including free shipping for purchases over $50.
Pure Encapsulations’ Digestive Enzymes Ultra has been described to be a “comprehensive digestive blend” which “helps break down fats, carbohydrates, fiber and dairy“. One bottle contains 180 vegetarian capsules, which do not contain any artificial additives, allergens, environmental contaminants or added excipients.
It is said to have a comprehensive digestive blend due to featuring a blend of 13 different enzymes – including amylase, protease, protease 6.0, glucoamylase and lactase – which also help in maximizing absorption.
2. Best Budget – NOW Super Enzymes at Amazon

This product is sold at a retail price of approximately $11 for a single-pack with 90 capsules; approximately $20 for a single-pack with 180 capsules; and approximately $38 for a double-pack with 180 capsules per pack.
NOW has been a leader in the natural products industry since 1968, with a mission of providing value that empower people to lead healthier lives through its products and services. Therefore, NOW ensures that its dietary supplements, such as NOW Super Enzymes, are affordable and provide an effective way for its customers to get their daily recommended intake of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients.
NOW Super Enzymes has been recommended for those whose staples in their diets are fats, carbohydrates and protein. This is thanks to the supplement being formulated with Bromelain, Ox Bile, Pancreatin and Papain, which optimize in the breakdown of these three components.
3. Best Vegan – HealthForce SuperFoods Digestion Enhancement Enzymes at Amazon

This product is sold at a retail price of approximately $33 per bottle. One bottle contains 120 vegetarian capsules.
HealthForce is a reputable brand which promotes that its “hard-core, plant-based product line features supportive purifying products, vegan proteins, vital superfood formulas and high-quality single ingredient superfoods and herbal extracts.”
All of HealthForce’s products are:
- Pareve certified, which ensures that they have been made from certified kosher ingredients;
- Certified gluten-free;
- Oregon Tilth certified, which is a third party, non-profit certification service that inspects all stages of the production process;
- Certified vegan by Vegan.org, which ensures that no animals were harmed in the making of HealthForce’s products; and
- TruGanic verified; which is a third party, independent quality control certification which has accredited lab testing.
HealthForce’s SuperFoods Enzyme supplement is claimed to be the “ultimate enzyme support” from proteins and fats to amylase-resistant, hard-to-digest carbohydrates. The formula is 100% vegan and contains 15 different vegan, plant-sourced enzymes, which are active the moment the supplement is swallowed with food all the way to the GI tract.
4. Best for Lactose Intolerance – Lactaid Fast Act Chewable at Amazon

This product is sold at a discounted price of approximately $11 per bottle, in which its retail price is usually around $18, for a single-pack of 60 chewable tablets.
Lactaid is the #1 pharmacist recommended brand of lactose intolerance products, according to Pharmacy Times. The packaging comes in a single-dose portable packs. Each chewable tablet comes in a Vanilla Twist flavor and contains natural lactase enzyme which helps prevent bloating, nausea, diarrhea and gas as a result of consuming foods and beverages containing lactose.
How these tablets work is that they break down milk sugar, or lactose, into two simple sugars– glucose and galactose, to help reduce discomfort from dairy sensitivity and make it easier for the body to absorb, thanks to being formulated with 9000 FCC lactase units of lactase enzymes per serving size. The formula is also fast acting, which means that they start working from the first bite or sip of dairy.
However, it should still be consumed with precaution as the company’s statement that its product “prevents discomfort from dairy sensitivity due to lactose” has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Furthermore, the product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
5. Best for Vegetable-Associated Gas – Enzymedica VeggieGest at vitaminshoppe.com

This product is sold at a retail price of $34.99 per bottle. One bottle contains 90 vegetarian capsules.
Enzymedica‘s mission is to make great health easy for everyone. Therefore, they have ensured that every product line they own is:
- Clean – Enzymedica’s manufacturing processes and sourcing is independently audited by NSF International;
- Sustainable – Enzymedica’s headquarters and solar power is LEED-Gold Certified to ensure their carbon footprint is minimal and to maintain an ecological balance between their business and for their consumers;
- Effective – Enzymedica has developed pioneering technologies to improve the effective rate of their ingredients and independently verify them to ensure they meet quality standards.
Therefore, their VeggieGest enzyme supplement contains a high-potency enzyme, Alpha Galactosidase, which is “key in digesting the sugars from beans, grains, raw vegetables and other foods that create digestive discomfort.” The company also claims that VeggieGest “may assist the body in breaking down and assimilating these foods, which takes stress off the gallbladder, liver and pancreas.”
Other enzymes included in here are: Alpha Galactosidase, Glucoamylase, Cellulase Thera Blend, Protease Thera Blend, Maltase, Lactase, Invertase, Lipase Thera Blend, Pectinase, Hemicellulase and Xylanase.
What is the Difference Between Digestive Enzymes and Probiotics?
The common trait between digestive enzymes and probiotics is that they assist in digestion— they are absolutely vital in proper digestive health and supporting functions. However, it should be noted that the two are not the same.
Probiotics are benign living micro-organisms which live in our intestines; they are also referred to as ‘good bacteria‘. They actually have the capability of producing or encouraging the production of different types of enzymes, including digestive enzymes. They can also help minimize the amount of bad bacteria in the gut by colonizing and leaving less room for them, which, in turn, improves our absorption and reducing the risks of indigestion, constipation or diarrhea.
We can increase the amount of good bacteria in the gut by eating a diverse range of whole foods; increasing intake of vegetables and fruit; consuming fermented foods; lessening consumption of artificial sweeteners; eating whole grains; adopting a plant-based diet; eating foods rich in polyphenols; or consuming prebiotic foods.
What are Natural or Food Sources of Digestive Enzymes?
Some individuals may feel reluctant or simply choose not to consume supplements for various reasons, from being physically unable to, not liking the tastes of supplements to not wanting to rely on manufactured products from companies for their health.
Rest assured, there are natural alternatives to help obtain digestive enzymes and still achieve similar results. Below are some of the foods that contain natural digestive enzymes.
1. Pineapple

This tropical fruit is actually packed with digestive enzymes, particularly bromelain. These enzymes are also known as proteases, which has a function of breaking down protein into amino acids, making them easier to absorb by the body.
In one study, which had been conducted on individuals with pancreatic insufficiency– in which the pancreas cannot produce sufficient digestive enzymes, consuming bromelain combined with a pancreatic enzyme supplement helped to improve digestion more compared to consuming the pancreatic enzyme supplement on its own.
2. Papaya

Another tropical fruit, papayas also contain proteases that help break down protein into amino acids. Instead of bromelain, papayas instead have a group of proteases called papain.
Several studies have found that consumption of papayas may help ease symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)– which include pain and cramping, diarrhea and constipation. However, it is strongly important that papayas are ripe and uncooked before eating, as heat exposure can destroy papain and other digestive enzymes.
3. Mango

Also a tropical fruit, mangoes contain the digestive enzymes amylases. Unlike proteases which help digest protein, amylases are a group of enzymes which break down carbohydrates from starch, which is a complex carbohydrate, into simpler sugars, such as glucose and maltose.
These enzymes influence the sweetness of the mango; they become more active as the fruit ripens.
4. Honey

Consuming raw honey has the most benefits, as processed honey is likely to have had the honey undergo a heating process, which would have likely destroyed its digestive enzymes.
The digestive enzymes contained in honey include:
- Diastases: Degrades starch into maltose;
- Amylases: Breaks down starch into simpler sugars, like glucose and maltose;
- Invertases: Digests sucrose, a type of sugar, into glucose and fructose;
- Proteases: Breaks down proteins into amino acids.
5. Bananas

Bananas contain amylases and glucosidases, which are two groups of enzymes that help break complex carbohydrates, such as starch, into simpler sugars, such as glucose, maltose and fructose. Similar to mangoes, these enzymes become more active as the fruit ripens; therefore, it influences the color of the banana skin peel and sweetness of the fruit.
In a study conducted over 34 women over a two-month period, it was found that those who had consumed two bananas daily experienced almost to no change in healthy gut bacteria and significantly less bloating.
Can Digestive Enzymes Help with Weight Loss?

Although digestive enzymes may not contribute directly to weight loss, research shows that enzyme inhibitors might. Digestive enzyme inhibitors are those that decrease the absorption of particular macronutrients.
For instance, according to a review of 14 studies, it was found that individuals supplemented with an amylase inhibitor, which had been extracted from white beans, may have increased both weight loss and fat loss.
Using inhibitors is sometimes used in treatment for obese individuals to support their weight loss.
In one study, which had 40 obese women adopt long-term use of the lipase inhibitor called orlistat, it was found that the level of hormones associated with suppressing hunger and appetite had increased.
Orlistat may also reduce fat absorption by 30%. This is because it decreases the production of lipase in the stomach and pancreas and, thus, results in weight loss.
Conclusion
Enzymes are highly important as they help catalyze reactions at a rate necessary for life. Having insufficient or an overabundance of enzymes can also be troublesome and lead to certain diseases or disorders. There are six classifications of enzymes, with digestive enzymes being one of them. Digestive enzymes and probiotics are not exactly the same, but both aid in digestion. As individuals may have disorders or intolerances due to the lack of the necessary digestive enzymes, supplements are available to assist in enabling smoother digestion and absorption of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients. However, it is important to consult with your doctor or physician before consuming any supplements, especially if you are pregnant or have any allergies.
References
- “Enzyme,” National Human Genome Research Institute
- “The Central Role of Enzymes as Biological Catalysts,” NCBI
- “Enzymes,” Biology LibreTexts
- “Enzymes,” Biology Reference
- “Enzymes,” Byju’s
- “Oxidoreductases: Overview and Practical Applications,” Hina Younus
- “Oxidoreductase Protein Complexes,” Biology LibreTexts
- “Transferases,” ScienceDirect
- “Hydrolases,” ScienceDirect
- “Exploring the chemistry and evolution of the isomerases,” NCBI
- “Ligase,” BiologyOnline
- “Digestive enzymes,” Science Learning Hub
- “The Health Benefits of Digestive Enzymes,” Very Well Health
- “The 9 Best Digestive Enzymes of 2020,” Very Well Health
- “Probiotics vs. Digestive Enzymes,” Probiotics Learning Lab
- “Digestive Enzymes vs. Probiotics: What You Need to Know,” Dr. Ian Stern
- “10 Ways to Improve Your Gut Bacteria, Based on Science,” Healthline
- “12 Foods That Contain Natural Digestive Enzymes,” Healthline
- “Do Digestive Enzymes Promote Weight Loss?,” Healthline
