What are TED Stockings?
If you are still fairly new to compression socks, then there are several terms you have heard before. You will have heard of toeless, varicose veins, deep vein thrombosis, and TED stockings. TED stockings are a term that you will hear very often and with good reason. TED is actually an abbreviation for thromboembolism-deterrent. Therefore, TED stockings are thromboembolism-deterrent stockings.
TED Stockings
TED stockings are a specially designed pair of socks that are built to support the venous and lymphatic drainage of the leg. This means that when you are recovering in bed from an injury or surgery, these stockings will help stop blood clots from forming. Also, if you are non-ambulatory, the combination of gradient compression and actual muscle pump effect of your calf help circulate blood and lymph fluid through your legs.

TED hose vs Regular compression socks: The difference between TED hose and regular compression socks is that compression socks are made for people who can still walk. Nurses, and teachers who naturally have tired feet due to their demanding lifestyle use compression socks to relieve their muscles. Compression socks are also used to manage symptoms of diseases such as edema, and varicose veins. Overall they provide proper circulation to the heart by the veins.
TED hose, on the other hand, is a specialized version of compression socks. The basis of their construction is primarily compression. However, they are altered to fit the needs of patients who are bed-ridden. TED hose work to ensure that circulation is consistent so that the blood does not slow down; which in turn prevents the formation of blood clots.
Deep Vein Thrombosis

The term TED hose is often followed by the name Deep Vein Thrombosis. The two are closely associated as deep vein thrombosis or DVT is a condition that centers around blood clots and the veins. The body has two main types of veins; superficial veins, and deep veins. Superficial veins are located close to the surface of the skin. They often turn varicose when they are put under pressure due to the backflow of blood. The deep veins are hardly affected by varicose veins, however, they can be affected by a dangerous condition known as DVT. Deep vein thrombosis is a condition where a blood clot or thrombus forms in one of the deep veins of the body. A blood clot forms when a clump of blood turns solid.
Reasons for blood clot
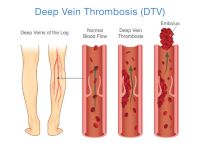
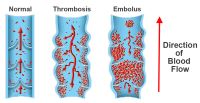
There are many reasons why a blood clot would form in one of the deep veins of the body. One of the most common causes is the coagulation of the blood faster than usual. Coagulation is a term to describe the process of clotting. When you get a cut or a wound, proteins in your blood called fibrins work with small blood cell fragments called platelets to create a mesh-like network to stop the bleeding.
Hypercoagulation
When the bleeding has stopped, and you have healed, the body should break down the clots and remove them. unfortunately, this whole process can be affected by deficiencies or increases in the proteins or platelets. Blood clots can sometimes form to easily or fail to break down properly. This is what is known as Hypercoagulation.

Hypercoagulation is caused by either an acquired source or a genetic source. An acquired source means that it was triggered by an external agent; the most common one is the use of certain medications such as birth control pills. Smoking is another acquired source, as is trauma to the vein, fracture to the leg or arm, bruising, and complication of an invasive procedure of the vein.
Genetics
Genetics can also cause hypercoagulation. This is very rare but genetic defects cause excessive clotting of the blood. These are usually blood disorders that are inherited and can be passed down to other family members. These defects usually occur in the proteins needed for blood clotting and can also occur with the substances that delay or dissolve blood clots.
Immobility
The other cause of DVT is immobility. Being immobile means that you cannot be on your feet at all, or only once in a while for some time. Immobility is dangerous for the veins because they are responsible for transporting blood back to the heart. They do this through the help of the leg muscles. Activities of walking, running, and other exercises activate the muscles which in turn helps the veins to push the blood back to the heart. When the muscles are at rest, blood starts to slow down.
Immobility is common in some types of people; for example pregnant women. Doctors can recommend bed rest for pregnant women a few months before they deliver the baby. More than that, they are required to stay in bed 6 to 8 weeks post-partum after delivery of the baby. Being off your feet for this long drastically slows down your blood giving it a higher potential for forming blood clots. If you are a person who travels a lot, then you spend most of your time sitting down or lying down. This puts your muscles at rest which slows down blood flow and increases chances of forming blood clots. Hospitalization, surgery, and obesity are other factors that could cause immobility.
Signs and Symptoms

The first thing that people with DVT experience is a pain in their thigh or lower leg, depending on where the clot has formed. This pain often starts in your calf and can feel like cramping or soreness. The affected leg will also start to swell; very rarely do both legs swell. Next, you will notice that the affected area will feel warm or hot to the touch. This will be followed by severe discoloration of the affected area. it will turn red, then bluish or whitish. leg pain will worsen when you bend the affected foot. Unfortunately, some people do not realize that they have DVT until they get symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism.
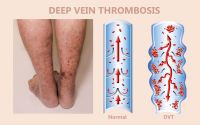

A pulmonary embolism happens when a blood clot from deep vein thrombosis breaks off and travels through the bloodstream to the lungs. This becomes a life-threatening condition because the clot blocks an artery in the lungs. A pulmonary embolism causes sudden shortness of breath especially when you walk, or run. You will experience severe pain in the chest that worsens when you take a breath or cough. You may also cough up blood, feel lightheaded or dizzy, and have a rapid pulse.
TED Hose
As mentioned before, TED hose are a specially designed type of compression wear that prevents the formation of thrombosis in the veins of the legs. They work just like compression socks do. They are made from elastic fabrics that make them tight and snug when you wear them. TED stockings are tightest at the ankles and least tight where they start (thighs, waist, or knees). This is what is known as graduated pressure. When you wear TED hose, the pressure they apply press on to the veins. Due to the applied pressure, the veins reduce in diameter size which increases the pressure of blood flow.
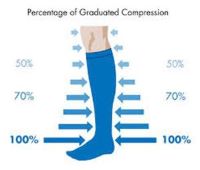
An increase in blood pressure means that it flows as it should. When circulation is consistent, there is a smaller chance that blood clots will form. TED hose are good form people who are at risk of developing DVT. If someone in your family has developed DVT before then you are at risk of developing DVT. To prevent this, you should consistently wear a pair of TED hoses. People who fly a lot such as pilots, and stewardesses, or if you travel often, you will be sitting or lying down often. To prevent the formation of blood clots in the veins, you should wear a pair of TED hose when you travel.
Popular Articles on ComproGear
What Level of Compression Socks Do I Need? Highest Compression Socks
TED Hose Sizes
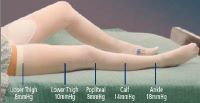
Like any other pair of compression socks, you need to measure your legs to determine the right size for you. Getting a size that is too big will not help with slowed blood flow. A size too small will instead cut off circulation to the heart. If you can get a professional to measure your legs, it is best to go with that option. If you measure your own legs, start with the ankle measurement; it should always be your first measurement. Measure around your ankle for the ankle circumference. It should be at the narrowest part of your ankle. Next, take your calf measurement by measuring the widest part of your calf. The thigh measurement is the next measurement. It should be done at the fullest part of your thigh, right under the buttocks.

Next, measure your buttocks at the fullest part to get the hip measurement. Next, measure your preferred waistline, it should be where you wear your pants most comfortably. Finally, measure the distance from your waistline to the floor to determine the proper length of your hose. Once you have these measurements, you can determine which TED hose sizes are perfect for you. Picking out the right size is also about wearing the hose. TED hose is made to be thicker than the regular types of hose. Therefore, when you go to buy these compression socks, ensure that you go with a pair of shoes to determine whether they fit well.
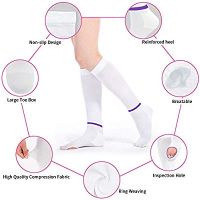

TED hose sizes are constructed with graduated pressure with pressure level being highest at the ankles. The clinically proven pressure pattern has a pressure level of 18mmHg at the ankles. The calf has a pressure level of 14mmHg while the popliteal has a pressure level of 8mmHg pressure level. The lower thigh has a pressure level of 10mmHg and the upper thigh has a level of 8mmHg. Ted hose sizes are also determined by pressure levels. TED hose are available in 20mmHg pressure level and below. Those who wish to prevent symptoms of DVT should get any of the pressure levels in that group. Before buying a specific pressure level however, you should consult a physician to advise you on what level is better for you.
How to Wear TED Hose

After you have bought the right pair of TED hose, you can now put them on. Insert your hand into one of the legs of the hose as far as the heel pocket. Grasp the middle of the heel pocket and turn the hose inside out to the heel area. Position the hose over the foot and heel. Ensure that the heel is centered in the heel pocket. Next, pull a few inches of the hose up around the ankle and calf. Continue pulling up the hose gradually ensuring that the hose glides up smoothly. If your skin feels a little dry, you can put on a layer of lotion to ensure that they glide up smoothly. If your skin is wet, use some baby powder or cornstarch to absorb that moisture.
As you reach the thigh portion of the hose, start rotating the hose inwards so the panel is centered over the femoral artery. The panel is placed slightly towards the inside of the leg. Pull them up slowly until they land on the waist. Straighten out the waistline and the buttocks. Check your hose to ensure that there are no wrinkles or bunching up. Wrinkles and bunching cut off circulation in the veins.
Caring for TED Hose

TED hose needs to be washed every day to ensure that they are clean. When you wash compression socks, you should always use cool water. Warm or hot water will alter the elasticity of the socks. Dip the hose in cool water then remove them. Add mild detergent soap in the water. Mix in the detergent with your hand then dip the stockings back in. Allow them to sit for 5 to 10 minutes. After soaking, gently rub the stockings to remove dirt and oil. Gently squeeze them out to remove excess soap; do not pull them as this will damage the elastic and they will become stretched. Rinse the socks in cool water to get rid of the soap. Do this until the water comes out clean when you squeeze them.
After you squeeze them gently to remove water, dab them with a clean towel to get rid of excess water. Finally, dry them by laying them flat somewhere cool to dry. You can also hang them somewhere to dry with a free circulation of air. Do not place them near any heat to prevent damaging the elastic.
This page last updated December 15, 2022
