If you get into some rehab facilities, hospitals, and several other medical complexes, you might have noticed that many patients housed in these facilities are wearing either anti embolism socks or compression stockings. Unfortunately, the majority of these patients aren’t correctly wearing their socks. And many of the patients, when told that they aren’t on the right socks, eventually ask: “What is the difference between anti embolism stockings and compression stockings?”
Compression Socks and anti embolism stockings are specialized types of hosiery mainly designed for this identical use: Compression. Regardless of this similarity, several factors set them apart. The analogy has influenced how people view these socks. As their needs grow and their utilization expands into several professions and conditions, there are continuous misconceptions and confusion about these stockings – Compression socks and anti embolism stockings.
We understand how confusing they could be; thus, we felt it would be beneficial to shed some radiant light on this subject and just discuss the substantial differences and the actual purposes of regular stocking and anti embolism socks (TED) Hose briefly.
What is the Difference Between Anti embolism Stockings and Compression Stockings?
For simplicity and clarity, we’ll start this section by analyzing each sock. We’ll begin with anti embolism socks. After that, we’ll explain compression stockings and then highlight some of the differences. And finally, we’ll highlight how to maintain them.
Anti embolism Stockings
To better assist in the distinguishing of anti embolism socks from other regular types of socks, they are manufactured only as white socks purposely. Also, another characteristic of these socks is that they are also designed with an inspection hole in the toe region for convenient monitoring of the patient’s circulation and other signs.
The Purpose of Anti Embolism Stockings
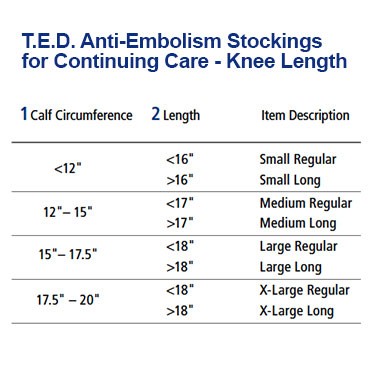
TED stockings are primarily designed as a preventive measure for bedridden patients. These are intended impressively to prevent VTE (Venous thromboembolism). The most usual type of this fatal condition is a blood clot in one of the veins, refers to as DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis).
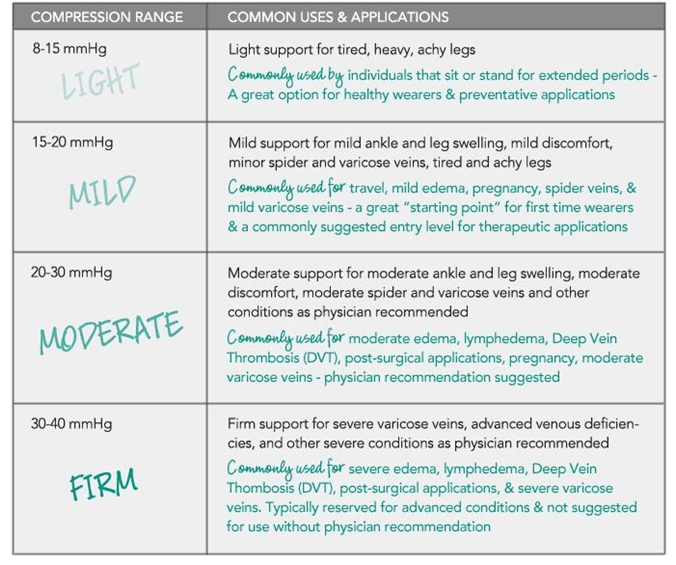
Anti embolism socks wouldn’t guarantee sufficient compression socks for folks that usually sit or stand for long hours each day. These individuals will require a compression level ranging from 20-36mmHg or even in some cases, a higher compression so that their level of severity and complexity could be worked upon.
When To Wear TED Stockings?
Only patients that are immobile or spends excessive time in bed for several days could have TED’s prescription. A physician in charge of your health care would tell you the right time to wear your TED socks, either during the daytime or nighttime, and the duration for wearing them, and when to wear them, either after an operation or before surgery.
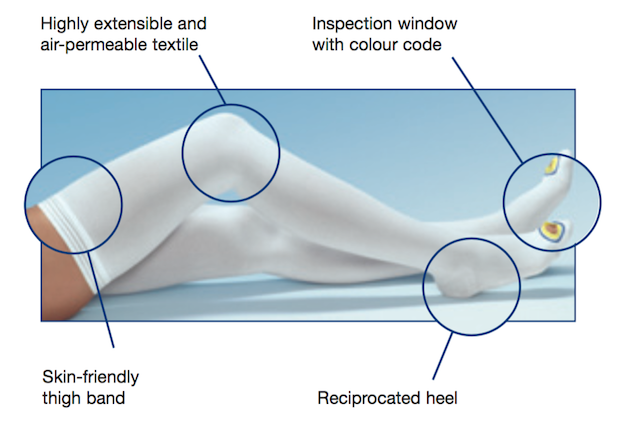
The fundamental purpose of these stockings is to halt the pooling of blood in the leg and limit blood clotting in the leg region. The risk for this is highly increased during or after a hospital stay due to a leg or pelvic surgery.
Sadly, a blood clot is dangerous. After breaking loose inside the vein, they can transfer to the lungs and heart where they can deposit and lead to pulmonary embolism (PE), which can lead to significant damage in the system or lead to fatality in an extreme occasion.
Usually, Ted stockings are often not meant for long term application on a patient. Featuring graduated compression that ranges from 8-15mmHg, the graduated compression is the peak in the ankle region, while it steadily lessens moving further up the leg.
One concern that has been given about anti-embolism stockings is that they can be tough to wear for individuals with limited strength in the hands and those with arthritis. With bedridden individuals, that isn’t an issue since medical staff, and other caregivers are often available to assist with the doffing and donning of the TED stockings.
Some wearers claim that the stockings they use don’t always stay well, regardless of the holdup band used or given, and on several occasions, they have to be adjusted throughout the day. As with other types of compression socks, the right measurement is essential so that a person can maintain a good fit of the socks to disallow rolling or pinching from the stockings which will also lead to a tourniquet effect, thus counterproductive for the patient.
Caution: Like other regular types of compression socks, anti embolism stockings are not ideal for all individuals. For instance, patients with PAD (peripheral artery disease) aren’t recommended to wear anti embolism socks since the blood supply to the leg is further compromised.
Regular Graduated Compression Socks
Different from anti embolism stockings, graduated compression socks are designed for folks who are capable of walking around, medically known as being ambulatory. This could be the condition with patients that have long been released from the hospital or other health care facilities. If they desire to keep on wearing graduated compression socks, their physician would advise them on the type of compression socks – pantyhose, thigh-high, or knee-high style, that would be well suited for them, regarding their situations. Besides, the physician can also examine the correct level of compression that should be worn for the exact result and comfort.
The Purpose of Wearing Compression Socks

Compression Stockings are often available for a preventive measure concerning a patient’s condition. Also, the treatment, usually long term, handles a wide range of conditions. Modern-day compression socks and complete length compression pantyhose are designed in a variety of fashionable colors, design variations, and styles with pressure classifications.
Other Differences Between Anti embolism Stockings and Compression Stockings
To comprehensively answer the question, what is the differences between anti embolism stockings and compression socks, at this stage, there are several other differences between anti embolism stockings and compression stockings that will be essential for us to verify. Thus, let’s examine other factors apart from the purpose we’ve considered. These include:
- Level of Compression
- Design
- Duration of use.
Level of Compression
Compression levels for anti embolism stockings and compression stockings are both measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) yet, there are differences. Between the two stockings, Anti embolism socks often have lower compression at around 8 to 18mmHg, on the other hand, compression socks have levels ranging from 15-20mmHg, 20-30mmHg and 30-40mmHg. However, before a person could be administered a compression level higher than 20mmHg, he or she has to obtain a physician’s correct prescription.
Design
Due to their different functions, they have marked differences when it comes to style and design. Compression socks are often available in varieties of colors and styles. However, anti embolism stockings are only available in white color.
Furthermore, the design of Compression stockings and anti embolism socks make them efficient for both Ambulatory patients and Non-ambulatory patients, respectively. As the socks move up to the leg, the compression structure of anti embolism changes, thus making it unsuitable for mobile patients.
Length of Use: The duration of use varies from one condition to another. But in general, anti embolism socks are designed for a short-term application, using it for at least three weeks, or until a need arises. However, compression socks can be used for more than six months, depending on the recommendation given by a doctor.
Maintaining and Caring Guidelines for Anti embolism stockings and compression stockings
If you’re administered any of these socks, what are the maintenance and care options? Let’s consider them:
Washing

- Do not use bleach or softener
- Daily washing is vital. If you can’t, wash every two days.
- Hand-wash your stockings. However, if you will use a machine, set it to a gentle cycle.
- Use standard detergent and then without additives; some have recommended dish soap.
Drying

- Loosely layover vent or hang out to dry.
- After washing, place stockings on a fluffy towel, and after that, gently roll to get rid of excess water
- Do not put dryer socks in the microwave or dryer.
Wearing
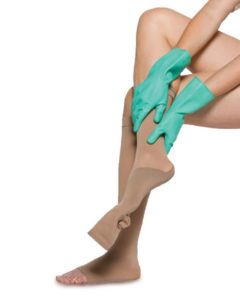
- Use gloves to smooth out the socks to evenly distribute compression and get rid of wrinkles.
- Rubber gloves must be worn if you want to wear your stockings
- For knee-highs socks, leave two finger widths between the top and knee of socks
- Use the “heel pocket out” style to don the socks.
Why Identifying the Right Type of compression is Vital
If you were asked, how much water does your body require, what would you say? You might be stunned to hear that your body is made up of 50 – 65% of water. And an approximate of 20% is available in the blood plasma. Another essential fact is that nearly two-thirds of the water is present within the cells of one’s body while the other third is outside. Is it difficult to see the vitality of water for good health?
Water plays an incredible role in transportation in the body and help in several chemical reactions. Thus it must mobilize and circulate efficiently throughout a person’s body. This is obtained via a lot of mechanisms. And one of the devices is linked with pressure. If the internal pressure isn’t accurate, water will be retained in the region where it isn’t needed; this usually occurs in the ankles and legs region. This reaction can lead to the appearance of swelling. Of course, this can be present in other parts of the body too. Often, this build-up may be harmless. However, it could be a signal something more chronic.
A simple way to examine if your condition is harmless or harmful is by examining the external and internal causes of pressure changes in the system. For instance, an external force on the body is often gravity. Ideally, when a person is active and moves from one place to another, the effect of our body circulation is healthy.
Nevertheless, when immobilized for a time, the internal pressure would drop in comparison to a relative increase in external pressure. This could lead to pooling of fluid in parts of our body, and can later manifest as swollen arms, legs, and puffiness in parts of the body like the face.
The fundamental underlying cause is relatively harmless and external. Additionally, it is usually temporary, and as the external conditions change, the body will finally get to its sound and initial stage. But if the pressure changes on your body emanate from internal factors, then it can be dangerous.
For instance, insufficient pressure in the veins could lead to leaky fluid in the surrounding tissues. In some cases, it could result in congestive heart failure, where the heart’s contraction can’t pump blood around the body efficiently, and thus, it gathers close to the front of the heart.
Since your kidney plays a significant role in regulating water in your body. Therefore, kidney disease will influence the function and can result in edema. There are several other cases, though, but the essential thing is to consult your doctor if you notice swelling, especially if you have health issues.
How Much Compression is Required After Noticing?
This is one key question that needs to be asked by people seeking to use either anti embolism stockings or compression socks. The answer, however, relies on the underlying condition a patient is suffering from. And as a result, the strength of compression is often prescribed by physicians as they often do for medication.
Compressive strength can start from 20mmHg to 40mmHg in some cases, and can also be reasonably gentle. However, some persons could be given custom compression garments that could give them even pressure. Regardless, the primary aim of the compressor is to restore the circulation of fluid and restoration of pressure within the body, which is vital for health.
Popular Articles on ComproGear
How Long to Wear Compression Socks for Edema Compression Socks for Fluid Retention
Conclusion
As I’ve cleared the confusion between anti embolism socks and compression stockings, I’m quite confident that when next you are asked: “what is the differences between anti embolism socks and compression stockings, you will not just have something to say, what you will say will be substantial, accurate, and informative. This knowledge can smoothen any session you will have with your physician. And help you to be aware of your real need.
